The Astonishing Connection between Breathing and Memory
Jun 25, 2023
Breathe in, breathe out—it's a simple action we perform without even thinking. But recent scientific revelations have unveiled a captivating relationship between our breath and our memory function, shedding light on the intricate workings of our cognitive processes.
Groundbreaking studies have shown that the rhythm of our breathing has a profound impact on our neural activity, influencing crucial cognitive functions such as emotional processing and memory recall. The most astonishing finding? Inhaling, especially through the nose, can enhance our memory function. As this field of study continues to unfold, these remarkable insights could pave the way for innovative therapeutic approaches to combat cognitive decline and memory-related conditions.
Recent research has uncovered that the very rhythm of our breathing generates electrical activity in the brain, exerting a direct influence on emotional judgment and memory recall. Astonishingly, this effect is most pronounced during inhalation through the nose.
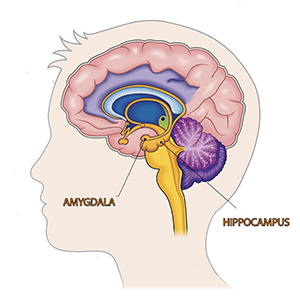
Scientists have identified the amygdala and hippocampus—regions of the brain intimately linked to emotion and memory—as significantly affected by the rhythm of our breath. These remarkable discoveries suggest that the act of breathing holds the power to modulate the functions of these key brain areas, thereby shaping our memory and emotional processing.
Intriguingly, controlled breathing techniques employed in mindfulness practices have also proven to be a potent catalyst for memory improvement. Mindfulness-based attention, which involves concentrating on one's breath, has been found to significantly boost working memory capacity—the type of memory we employ to retain and manipulate information over short periods. A study published in the Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology demonstrated that individuals who engaged in deep, intentional breathing exercises exhibited a heightened ability to maintain visuospatial information. This remarkable finding underscores the potential of controlled breathing as a tool to enhance cognitive performance.
 Lead researcher Christina Zelano, from Northwestern University, and her team conducted a series of experiments involving human subjects to uncover the profound impact of breathing on memory recall. Their results were staggering: memory recall was significantly better during inhalation compared to exhalation, with the effect being most pronounced when subjects breathed through their noses. These groundbreaking findings suggest that the act of breathing itself induces changes in the brain, amplifying emotional judgment and improving memory recall.
Lead researcher Christina Zelano, from Northwestern University, and her team conducted a series of experiments involving human subjects to uncover the profound impact of breathing on memory recall. Their results were staggering: memory recall was significantly better during inhalation compared to exhalation, with the effect being most pronounced when subjects breathed through their noses. These groundbreaking findings suggest that the act of breathing itself induces changes in the brain, amplifying emotional judgment and improving memory recall.
While the relationship between breathing and memory is still a nascent field, these discoveries open a world of exciting possibilities for future research and potential therapeutic applications. Unraveling the profound impact of breathing on memory could revolutionize interventions aimed at combating cognitive decline, stress, anxiety, and even conditions such as ADHD and Alzheimer's disease.
In conclusion, the mundane act of breathing—a function we often take for granted—holds a remarkably influential role in our cognitive processes, specifically in the realm of memory recall. So, the next time you find yourself struggling to retrieve information from the depths of your mind, take a pause, inhale deeply, and witness the astonishing power that our breath holds over our brains. It appears that in the realm of memory, our breath is far mightier than we ever imagined.
Breath Energy Newsletter
The Breath Energy Newsletter comes out on the first Friday of every month. It includes a conscious breathing practice, a body-mind topic and announcements.
Enter your email and sign up for free right now
No Spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

